Posterior Fossa Syndrome Braving Thursdays
Posterior Fossa Syndrome Together by St. Jude™
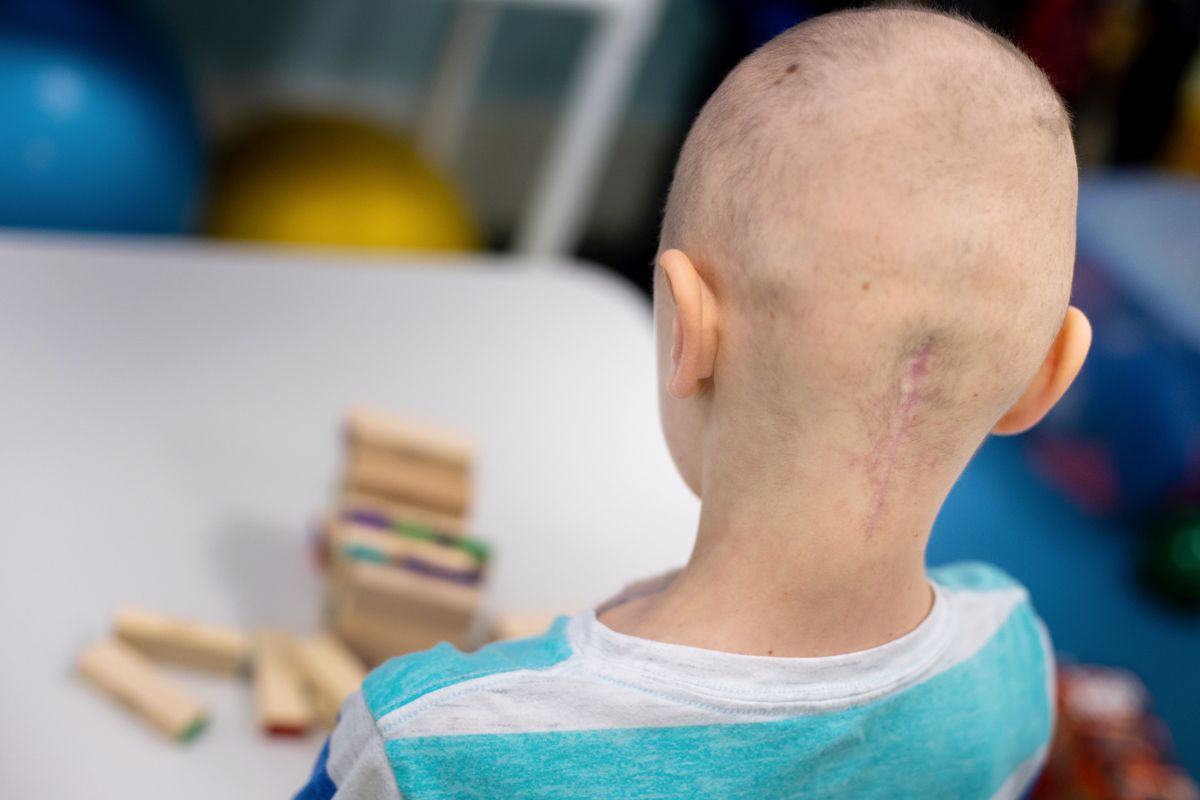
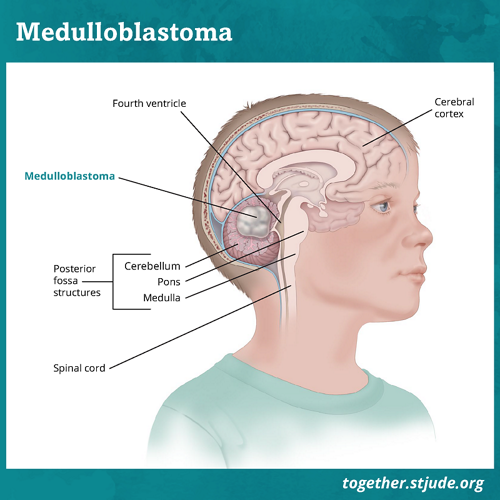
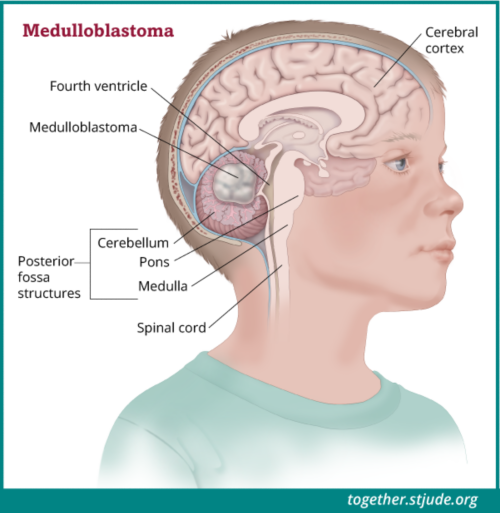
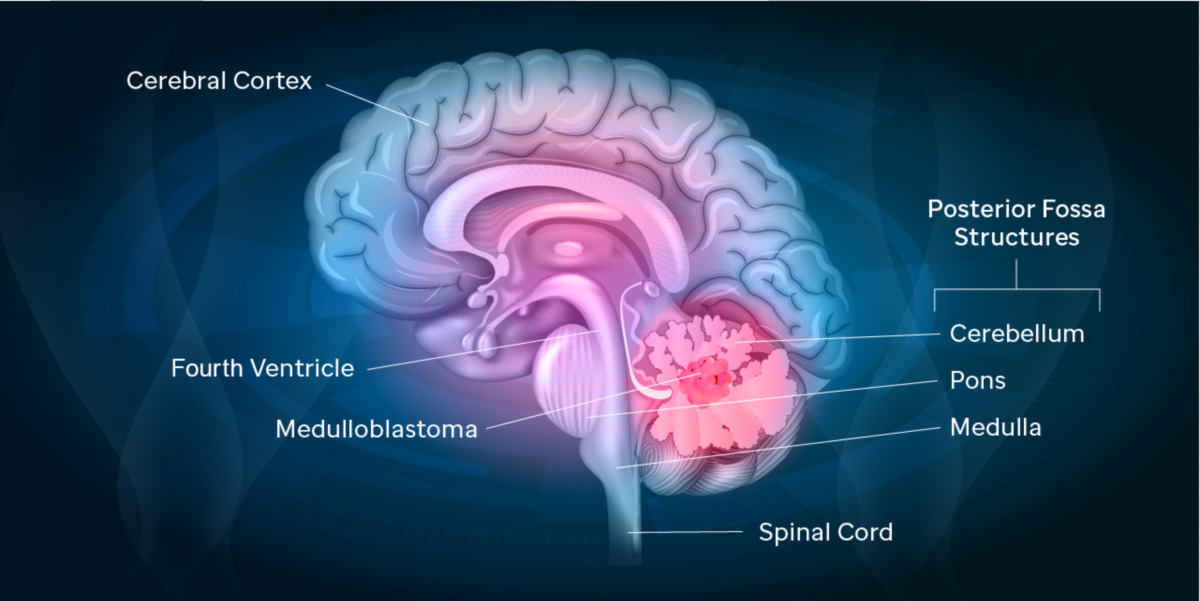
Posterior Fossa Syndrome: Review of the Behavioral and Emotional Aspects in Pediatric Cancer Patients Jane C. Lanier, MD1; and Annah N. Abrams, MD1,2 Medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood, occurs in the posterior fossa, the part of the intracranial cavity that contains the brainstem and the cerebellum.
Posterior Fossa Syndrome Together by St. Jude™
Posterior Fossa Syndrome (PFS), Cerebellar Mutism Syndrome, and Cerebellar Mutism are synonyms for a condition which can develop after surgery within the posterior fossa region of the cranium (Avula et al, 2015; Kupeli et al, 2011). The condition is characterized by a range of neurological problems such as: ataxia, mutism/dysarthria, hypotonia, emotional lability, and behavioral changes (Avula.

Posterior Fossa Cisterns The Neurosurgical Atlas
Medulloblastoma is the most common pediatric malignant brain tumor. 1, 2 Five-year survival rates are 70%-85% with treatment that includes surgical resection, risk-adapted radiation treatment, and chemotherapy. 3 Medulloblastoma arises in the posterior fossa region and the extent of the surgical resection is a good prognostic marker. 4 Thus, neurosurgeons will often strive for a gross total.

Posterior Fossa Society
Posterior fossa syndrome 4 Your child's rehabilitation team will include the following specialists: • Speech and language therapists can provide support for any speech, language and communication difficulties. In addition, they help with swallowing difficulties, supporting the process of eating and
Posterior fossa syndrome in children following tumor resection
Results: All surveyed professionals conceptualized posterior fossa syndrome as a spectrum diagnosis. The majority agreed that mutism is the most important symptom for diagnosis. However, results highlighted ongoing discrepancies related to important features of posterior fossa syndrome. Conclusions: Greater posterior fossa syndrome conceptual.

Posterior Fossa Syndrome Prognosis mapasgmaes
Posterior Fossa Syndrome (PFS) is identified by a collection of symptoms including reduced or absent speech, irritability, low muscle tone (hypotonia), unsteadiness and reduced coordination (ataxia) and the inability to coordinate voluntary movements. The condition can also be referred to as Cerebellar Mutism because of the significant impacts.
[Download 10+] 13+ Posterior Cranial Fossa Gif GIF
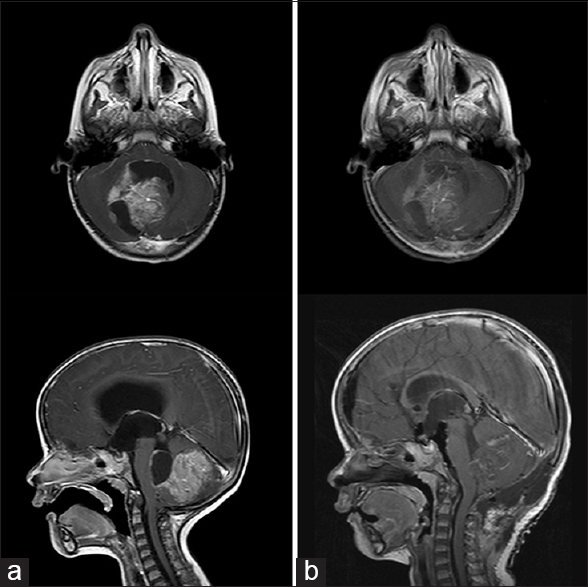
Posterior fossa syndrome (PFS), also known as cerebellar mutism syndrome, is a complication of surgery for medulloblastoma. While the syndrome is well known, its cause, features, risk factors, and manifestations are poorly understood. This prospective evaluation of 178 patients gives an unprecedented look at the clinical characteristics of the.

(PDF) Modafinil in the rehabilitation of a patient with postsurgical
Posterior fossa syndrome is a condition that's made up of a number of different symptoms. It can sometimes be the result of surgery to remove tumours from the posterior fossa area in the brain. It develops in around 25% of children with medulloblastoma, with symptoms generally appearing one to three days after surgery..
Posterior fossa
The history of posterior fossa mutism remains an enigma. While Harvey Cushing's contribution to the surgery of posterior fossa tumors dates back to almost a century, it is only in 1948 that Cairns and then in 1958 that Daly and Love described cases of patients with symptoms of akinetic mutism following posterior fossa surgery. 1 However.

Posterior Fossa Veins The Neurosurgical Atlas, by Aaron CohenGadol, M.D.
Posterior fossa syndrome occurs with medulloblastoma tumors that arise from the midline section of the lower part of the brain, which separates left and right cerebellar hemispheres. Also known as cerebellar mutism syndrome, this condition is best known for mutism since the affected child often loses the ability to talk after surgery. However.
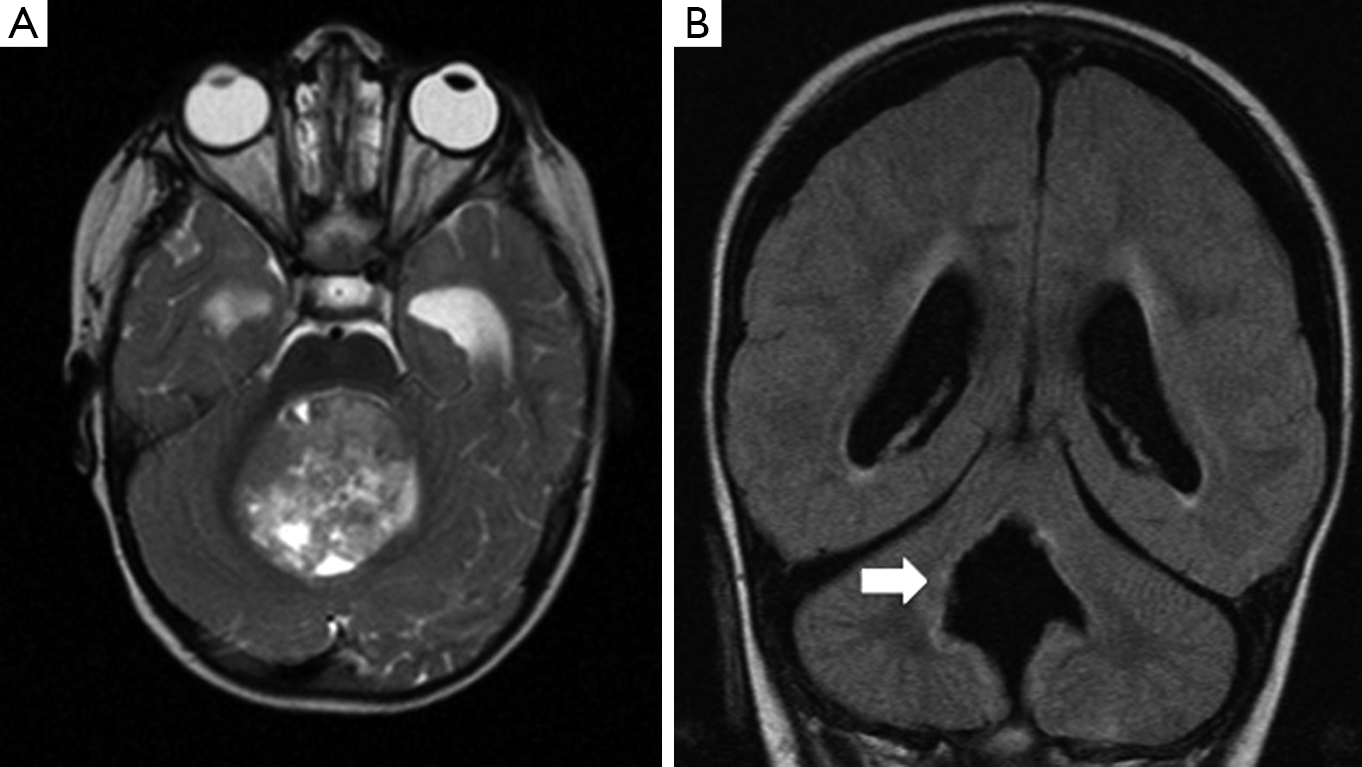
[View 50+] View Posterior Fossa Syndrome Images cdr MUHAMMADIYAH
Posterior fossa syndrome (PFS), or cerebellar mutism syndrome (CMS), is a collection of neurological symptoms that occur following surgical resection of a posterior fossa tumour, and is characterised by either a reduction or an absence of speech. Some authors suggest that CM is only one symptom of the CMS complex that also includes ataxia.
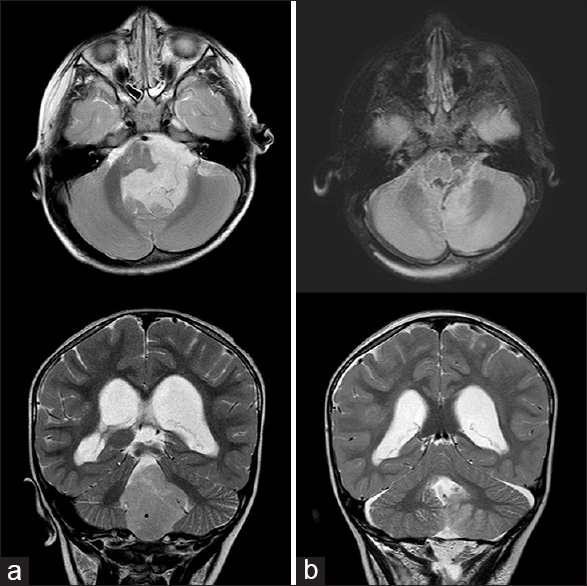
Posterior fossa syndrome in children following tumor resection
The Posterior Fossa Society will be hosting an open state-of-the-art conference on pediatric post-operative CMS and the CCAS in Liverpool, 11-13 June 2021. See here for further details. For marketing purposes the terms Cerebellar Mutism and Posterior Fossa Syndrome are used in some of the advertising material.
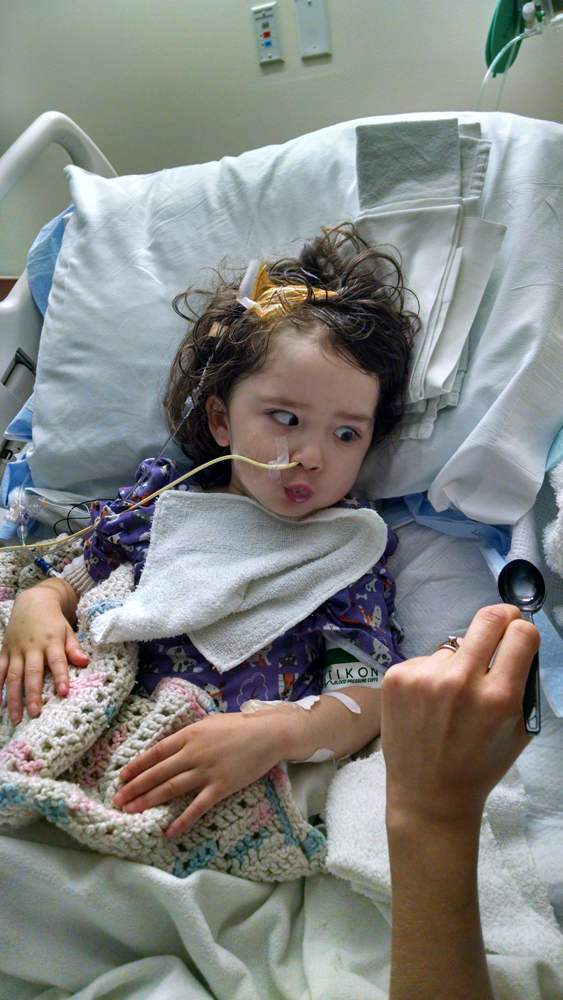
Posterior Fossa Syndrome Braving Thursdays
Posterior fossa syndrome (PFS), or cerebellar mutism syndrome (CMS), is a collection of neurological symptoms that occur following surgical resection of a posterior fossa tumour, and is characterised by either a reduction or an absence of speech. Some authors suggest that CM is only one symptom of the CMS complex that also includes ataxia.
Getting to the bottom of a medulloblastoma mystery St. Jude Progress
Posterior fossa syndrome (PFS), or post-operative pediatric cerebellar mutism syndrome, is characterized by mutism or reduced speech and mood/affect change after cerebellar or fourth ventricular tumor resection with potential long-term effects. Other features may include motor dysfunction (i.e., hypotonia, ataxia, and apraxia), brainstem.

[View 50+] View Posterior Fossa Syndrome Images cdr MUHAMMADIYAH
Posterior fossa syndrome is the name given to a collection of symptoms that may occur in children after they have had surgery at the back of the brain. What causes posterior fossa syndrome? The exact cause of posterior fossa syndrome is unknown; however, some evidence suggests that it is due to a disruption in signals in the brain that are responsible for processing information, sensations and.

Posterior Fossa Syndrome In Children Following Brain Tumor Resection
The final working definition identified delayed onset mutism or reduced speech accompanied by emotional lability after cerebellar tumor resection in children as fundamental features of the syndrome. 5 Mutism was noted to always be transient, though syndrome recovery may be prolonged. 5 Notably, the Posterior Fossa Society used "post-operative pediatric CMS" as the diagnostic label.